Introduction: The Dawn of Smart Agriculture
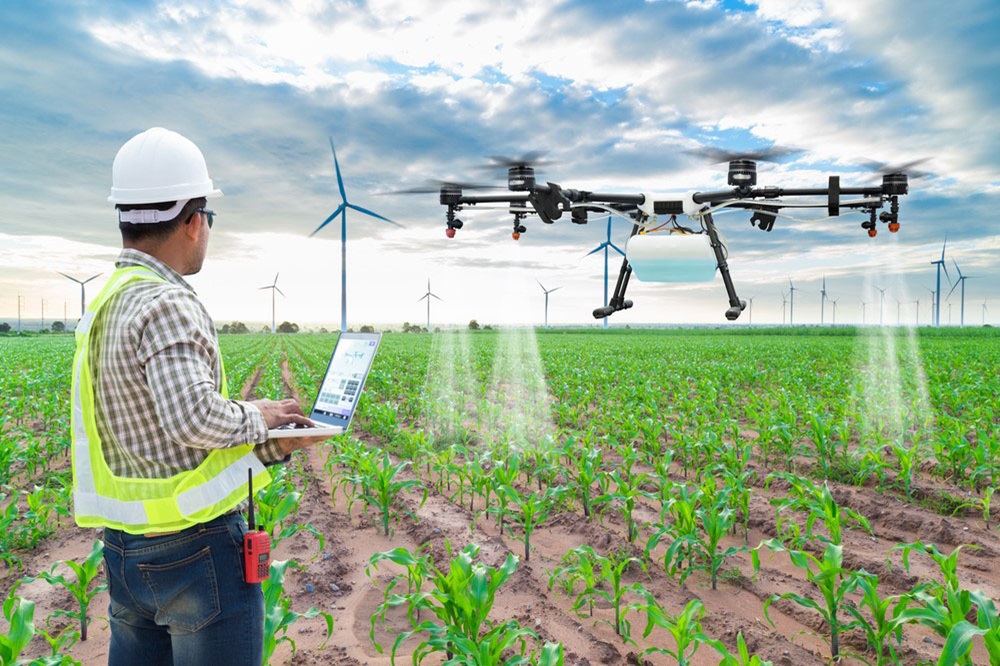
Agriculture has always been the backbone of human civilization, feeding the world’s population for millennia. However, as global demand for food increases and resources like land and water become scarcer, traditional farming methods are proving insufficient. Enter agricultural drones—the cutting-edge technology transforming how farmers monitor and manage their crops.
The use of drones in agriculture has sparked a revolution in precision farming, providing unprecedented insights into crop health, soil conditions, and pest management. With drones, farmers can optimize yields, reduce waste, and make data-driven decisions, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient future in agriculture.
This comprehensive article explores how drones are revolutionizing crop monitoring, delving into their benefits, applications, challenges, and the future of smart farming. By the end, you’ll understand why drones are not just an innovation but a necessity for the agricultural industry in the 21st century.
What Are Agricultural Drones?
Agricultural drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with advanced sensors and cameras that provide real-time data on crops, soil, and field conditions. These drones can cover vast areas in a short time, capturing high-resolution images and data that are analyzed using software and algorithms to gain actionable insights.
Key Features of Agricultural Drones:
- High-Resolution Imaging: Capturing detailed aerial images using multispectral and infrared cameras.
- GPS Integration: Enabling precise mapping and geolocation for targeted interventions.
- Data Analytics: Using AI and machine learning to analyze data for optimizing crop health and yields.
- Autonomous Flight: Pre-programmed flight paths for efficient, hands-free monitoring.
Traditional Crop Monitoring vs. Drone-Based Monitoring
To appreciate the impact of drone technology, it’s essential to compare it with traditional crop monitoring methods:
|
Aspect |
Traditional Crop Monitoring |
Drone-Based Monitoring |
|
Efficiency |
Labor-intensive, time-consuming |
Quick and efficient, covering large areas in minutes |
|
Data Accuracy |
Limited to visual inspections |
High-resolution data with multispectral imaging |
|
Cost |
High costs for labor and equipment |
Lower operational costs over time |
|
Sustainability |
May involve excessive pesticide use |
Enables targeted interventions, reducing chemical usage |
|
Scalability |
Challenging for large farms |
Easily scalable for farms of all sizes |
Key Benefits of Using Drones for Crop Monitoring
1. Real-Time Crop Health Monitoring
One of the most significant advantages of using drones is their ability to provide real-time data on crop health. By utilizing multispectral and thermal imaging, drones can identify stressed crops that might not be visible to the naked eye.
- Early Detection of Diseases and Pests: Drones can identify plant stress caused by pests or diseases before it spreads, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Improved Yield Forecasting: By monitoring crop health throughout the growing season, farmers can better predict yields and optimize harvest timing.
Case Study: A sugarcane farm in Brazil used drones to detect early signs of a pest infestation, saving the crop and boosting yields by 15%.
2. Precision Agriculture and Targeted Interventions
Drones enable precision agriculture, allowing farmers to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides only where needed, reducing waste and costs.
- Variable Rate Application: Drones equipped with sensors can generate prescription maps, enabling precision spraying of fertilizers or herbicides.
- Soil Analysis: By mapping variations in soil health, drones help farmers optimize planting patterns and nutrient management.
Case Study: A vineyard in France used drones to optimize water usage, reducing irrigation costs by 30% while maintaining grape quality.
3. Efficient Land and Field Management
Monitoring large fields manually is labor-intensive and time-consuming. Drones can cover hundreds of acres in a matter of minutes, providing farmers with a bird’s-eye view of their land.
- Field Mapping: Drones generate detailed field maps to assess topography, soil variability, and drainage patterns.
- Planting Optimization: Drone data can be used to optimize row spacing and crop density, improving overall field productivity.
Case Study: Australian wheat farmers used drone-generated field maps to identify areas of low productivity, optimizing seeding strategies and increasing yields.
4. Cost Reduction and Increased ROI
Investing in drones can lead to significant cost savings in the long run by reducing labor, optimizing inputs, and increasing crop yields.
- Lower Input Costs: Precision agriculture minimizes the overuse of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing input costs.
- High ROI: The cost of drones has decreased significantly, making them accessible to even small-scale farmers, with rapid payback periods due to increased efficiency.
Case Study: A soybean farm in the U.S. Midwest reported a 25% increase in profits after adopting drone-based crop monitoring.
5. Improving Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Agricultural drones contribute to sustainable farming by optimizing resource usage and reducing the environmental footprint of farming practices.
- Reduced Chemical Usage: By enabling precision spraying, drones reduce the overuse of fertilizers and pesticides.
- Soil Conservation: Monitoring soil health and erosion patterns helps farmers adopt more sustainable cultivation practices.
Case Study: A rice farm in India reduced its chemical pesticide usage by 40% through drone-based precision spraying, significantly reducing environmental impact.
Challenges in Adopting Drone Technology in Agriculture
While the benefits are clear, adopting drone technology in agriculture comes with its challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Many countries have strict regulations on drone usage, requiring licenses and airspace permissions.
- High Initial Investment: Despite the decrease in drone prices, the cost of high-end drones and sensors can still be prohibitive for small farmers.
- Technical Expertise: Operating drones and interpreting data requires training, which can be a barrier for farmers unfamiliar with the technology.
- Data Privacy and Security: As drones collect sensitive data about farms, concerns around data privacy and cyber threats need to be addressed.
The Future of Drones in Agriculture
As drone technology continues to advance, several trends will shape the future of smart farming:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI-powered drones will be able to predict crop diseases, optimize irrigation schedules, and automate planting.
- Autonomous Drones: Future drones will be fully autonomous, capable of flying and collecting data without human intervention, further increasing efficiency.
- IoT and Smart Farming Ecosystems: Integration with IoT devices will enable drones to interact with soil sensors, weather stations, and automated irrigation systems for a holistic approach to farm management.
- Blockchain for Crop Traceability: Drones combined with blockchain technology will ensure transparency and traceability in the food supply chain.
Future Vision: By 2030, drones are expected to be an integral part of farm management systems, contributing to increased global food production and sustainable agricultural practices.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Agriculture with Drones
The rise of drone technology in agriculture marks a new era in crop monitoring and precision farming. By providing real-time data, optimizing resource usage, and reducing costs, drones empower farmers to make data-driven decisions that enhance productivity and sustainability.
In a world where climate change, resource scarcity, and population growth challenge the global food supply, the need for smart agriculture solutions has never been greater. Drones are not just an innovative tool; they are becoming an essential component of the future of farming.
Farmers who embrace drone technology now will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive and resource-constrained world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can drones completely replace traditional crop monitoring methods?
- Drones enhance but do not fully replace manual inspections. They are best used in combination with ground-based assessments.
- Are drones affordable for small-scale farmers?
- Yes, the cost of entry-level drones has decreased, and many startups offer drone-as-a-service models, making them accessible to smaller farms.
- What crops benefit the most from drone monitoring?
- Drones are highly effective for crops like corn, wheat, soybeans, and rice, but they can be used for almost any type of crop.